
Purpose
To verify that the engine sensors and IPR are operating correctly within specified operating ranges The ECM will actuate the IPR and monitor ICP sensor feedback signals. If an ICP system problem exists, the ECM will transmit DTCs to the EST.
Tools
• EST with MasterDiagnostics® software
• EZ-Tech® interface cable
Procedure
NOTE: The KOER Standard test can only be done with the EST; MasterDiagnostics® software is required.
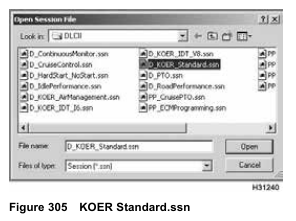
1. Open D_KOER_Standard.ssn to monitor engine operation.
2. Start and run engine to reach minimum operating temperature 70 °C (158 °F) or higher.
NOTE: Engine coolant temperature must reach 70 °C (158 °F) minimum for the ECM to accurately
test engine actuators and sensors. If engine coolant temperature is below self test range, the EST will display – Coolant temperature is out of range.
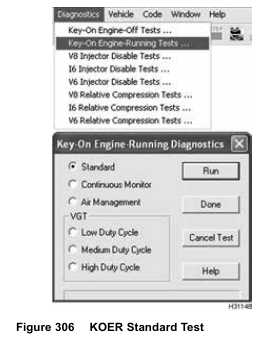
3. Select Diagnostics from menu bar.
4. Select Key-On Engine-Running Tests from the drop down menu.
NOTE: When using the EST to do KOEO or KOER diagnostic tests, Standard test is always selected and run first. If the ignition switch is not cycled, the Standard test does not have to be run again.
5. From the KOER Diagnostics Menu, select Standard Test and select Run to start the test.
6. The ECM will start the Key-On Engine-Running Standard Test and command the engine to accelerate to a predetermined rpm.
During the test, the ECM commands the IPR through a Step Test to determine if the ICP system is performing as expected. The ECM monitors signal values from the ICP sensor and compares those values to the expected values. When the test is done, the ECM returns the engine to the normal operating mode and transmits any DTCs set during the test.
7. Record DTCs on Diagnostic Form. See “Diagnostic Trouble Codes” – Appendix C (page 643) for DTCs.
8. Correct problems causing active DTCs.
9. Clear DTCs.
Possible Causes
• Oil leakage in injection control pressure system
• Loose or corroded engine wiring harness for ICP sensor or IPR valve
• Open or shorted wiring harness to ICP sensor or IPR valve
• Failed ICP sensor
• Inoperative IPR valve
• Inoperative high-pressure oil pump
• Not enough oil from lube oil system to high-pressure pump